-
workshop procedure
-
Enschede, Niederlande
-
BNA - De Branchevereniging Nederlandse Architectenbureaus
-
completed
-
2110-RVW
-
integral strategy
-
Piotr Kalbarczyk, Annika Brammer
-
Openfabric Landscape Architecture
Mijn WaterFabriek Systemen voor duurzam water
Kenniseiland, Enschede
DARE TO INNOVATE!
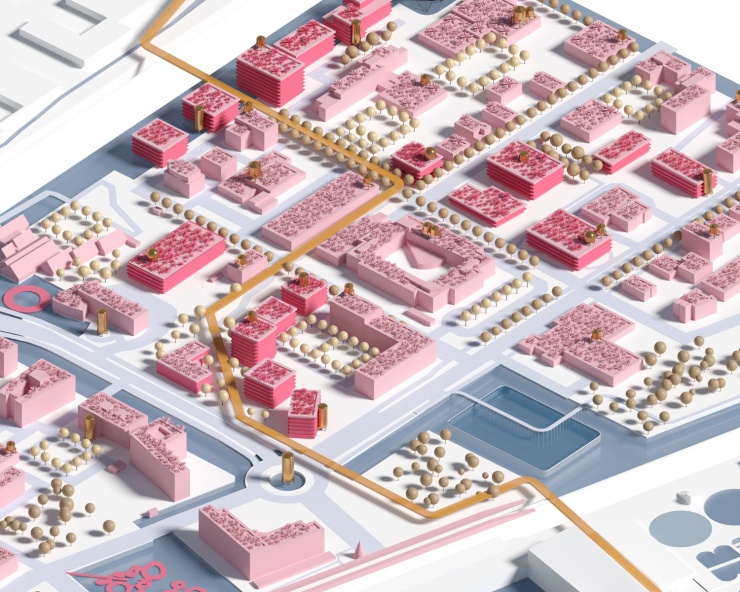
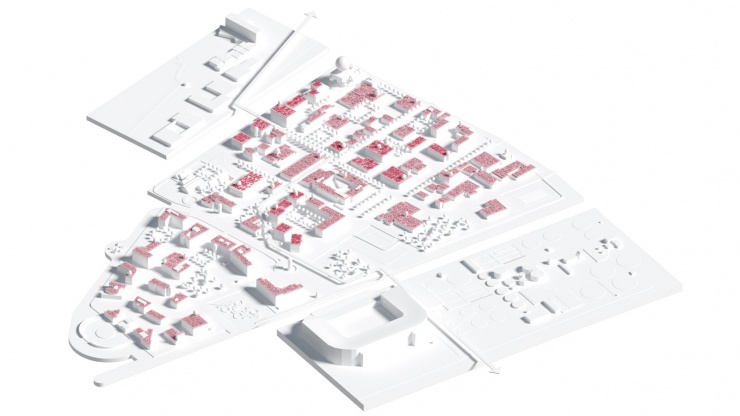
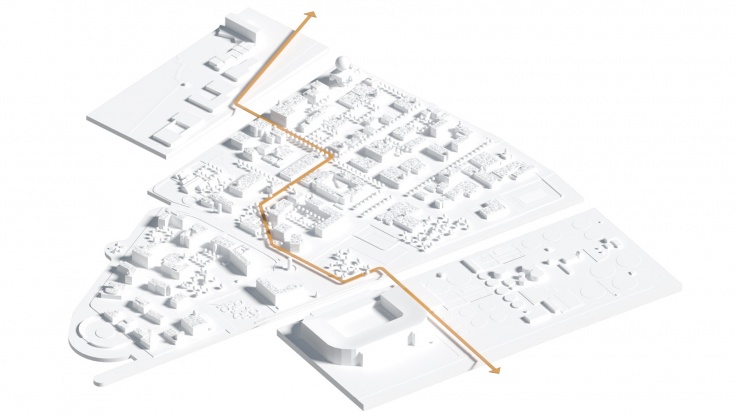
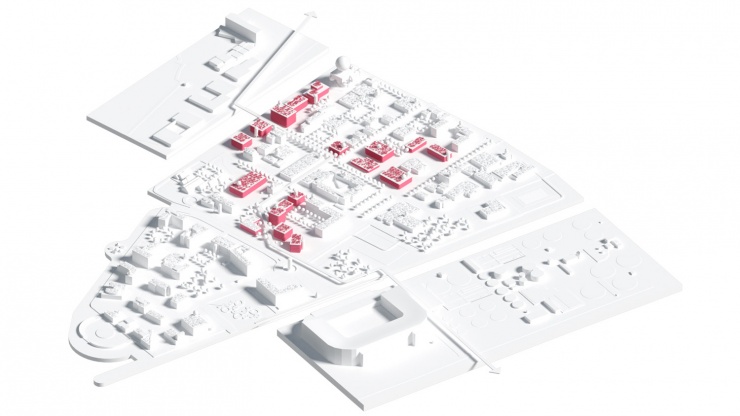
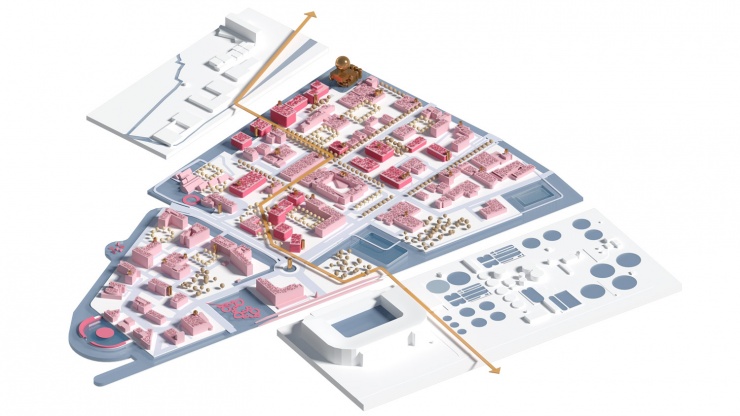
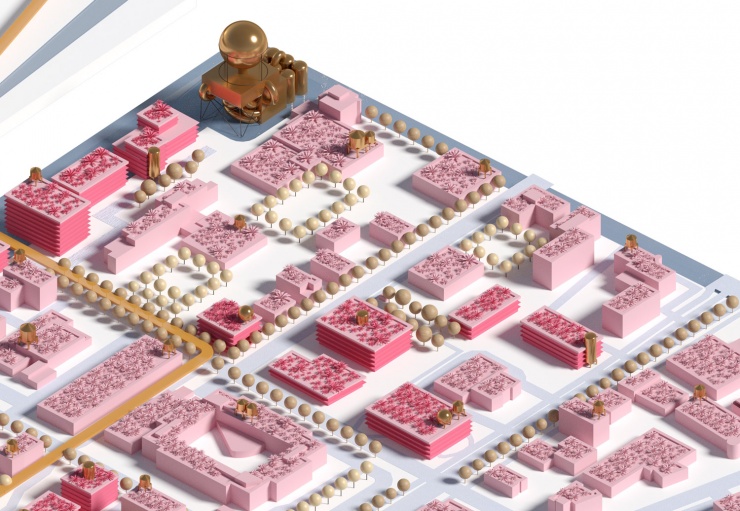
As a part of a workshop procedure, Cityförster, together with Openfabric Landscape Architecture and Mijn WaterFabriek Systemen voor duurzam water, proposed an integral strategy for the Business & Science Park of the Kennispark in Enschede that tackles not only the challenges of extreme weather conditions but also the energy transition towards a CO2-free built environment by 2050. The concept is based on the construction of a blue buffer around the location that creates more space for rainwater, recreation and reinforces the identity of the location. Together with a network of smart rain barrels and 'The Hub' arises an inclusive system that celebrates conscious water and energy consumption within a green-blue-minded environment.
CHALLENGES AROUND WATER MANAGEMENT
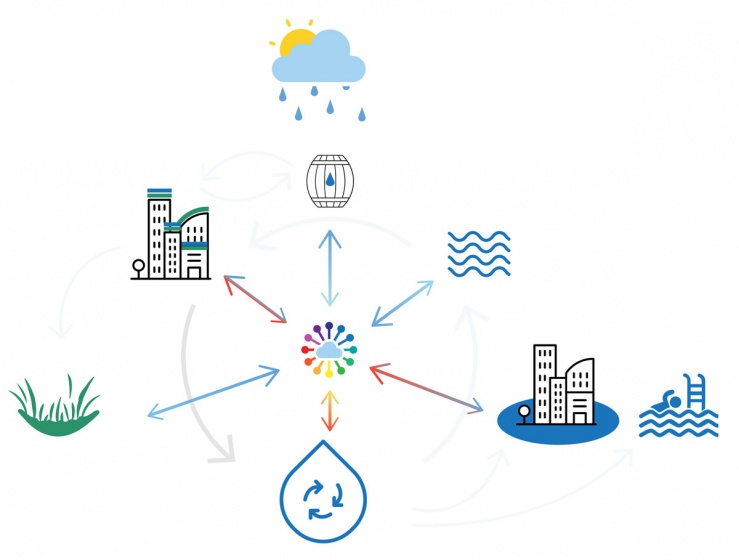
The capacity of our current sewerage system is not designed for extreme downpours. If there is an overload, in a mixed system, the untreated wastewater is dumped into the surface water together with rainwater. That is why it is better to retain the rainwater locally. By temporarily retaining rainwater locally, damage can be limited. The peak of the discharge of rainwater towards the sewer is shifted in this way: the rainwater only flows slowly towards the sewer pipe when it is empty again. Rainwater can be retained by constructing wadis, ditches, above-ground water buffers, green roofs, rainwater ponds, underground storage facilities, water squares, or rainwater use installations. Where soil conditions allow, the rainwater can also be infiltrated directly by softening and greening as much as possible. However, to limit damage during heavy cloudbursts, this must always be combined with other water-retaining facilities, especially in places where infiltration is not possible due to high groundwater levels.
On average, we use almost 135 liters of drinking water per day. Most of the drinking water is used for showering, flushing the toilet, and washing machines. Drinking is really just a little bit. A family pays an average of almost € 750 for the water supply: 30% of this is for the supply of drinking water, 26% for the sewage charge, and 44% for the purification and water system charges. Instead of disposing of clean rainwater with the sewer, you can also store and use it. Rainwater that falls on roofs is relatively clean. You can use it for the washing machine or the toilet, but also to water the garden. This way, it does not immediately disappear into the sewage system and it also saves drinking water. Furthermore, the consumption of water could be reduced by raised awareness among the citizens and businesses. It is also important to improve the efficiency use by e.g. installing water-saving showers and toilets. Greywater treated in wetland or through filters could also be reused.
You can find a link to a reader (Dutch) with all the results of the workshop here.
-
workshop procedure
-
Enschede, Niederlande
-
BNA - De Branchevereniging Nederlandse Architectenbureaus
-
completed
-
2110-RVW
-
integral strategy
-
Piotr Kalbarczyk, Annika Brammer
-
Openfabric Landscape Architecture
Mijn WaterFabriek Systemen voor duurzam water